NIELS BOHR (1885 - 1962 C.E.)

In 1913, Neils Bohr created a new model of the atom. It consisted of electrons that orbited in "shells" or layers around the nucleus. As the energy level changed, so did the location of the electron. Neils Bohr was also the first to introduce the idea of the quantum mechanical model, where a cloud of electrons surrounds the nucleus.
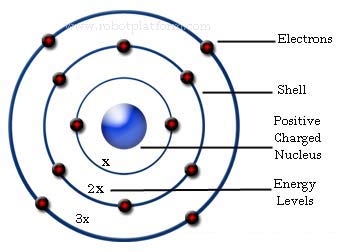
Neils Bohr developed the Bohr atomic model, with electrons travelling in orbits around the nucleus, and chemical properties being determined by how many electrons are in the outer orbits. He also integrated the Planck quantum theory, stating that when electrons change orbits they emit a quantum of discrete energy.

